Multi-network SIM cards are being used by businesses to provide seamless and reliable connectivity by enabling devices to switch between multiple networks for optimal connectivity. This flexibility is essential to a wide range of IoT applications, from smart cities and connected vehicles to industrial automation and healthcare.
What is a multi-network SIM card?
Traditional single-network SIM-cards are standard for cellular data on mobile phones but are also used in IoT devices. These SIM-cards, usually provided by a local operator, only allow you to access the network of that operator, whereas multi-network SIM cards roam across different networks per country. They enable seamless switching between networks without manual intervention to aim for optimal coverage and signal strength.
For example, a Dutch company providing parking meters to municipalities could use the multi-network SIM-cards to have coverage in all parts of the Netherlands. The parking meters could then access, for example, the KPN, Tele2 and Vodafone networks. If there is an outage, a parking meter would switch to a different network. If the parking meter is in a remote area, it would choose the network with the highest signal strength.
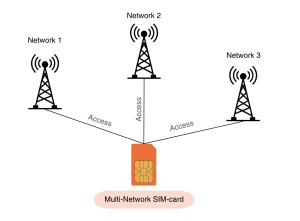
How do multi-network SIM-cards work?
Multi-network SIM cards have embedded profiles, which contain the profiles of multiple different mobile network operators, enabling it to connect to various networks as needed. Moreover, dynamic SIM provisioning allows for over-the-air updates and remote provisioning of the SIM cards.
Steered vs Non-Steered Multi-Network SIM-cards
Depending on the operator, a multi-network SIM-card can be configured to be either steered or non-steered.
- Steered: Parameters according to which the SIM card will choose which network to connect to are set by the operator
- Non-steered: SIM card can connect with any network in range without preference. The steering will then depend on the settings of the IoT device.
With non-steered SIM cards, it is often the case that the device will stay connected to the network it initially starts a session with. Only when it loses connection or is triggered (automatically or manually) to re-scan the networks, will it re-establish the best network according to the programmed parameters. Also, if no preferences are set in the IoT device, it is possible that the device will choose the first network it connects to, regardless of whether it is the best available option.
Network Coverage
MNOs and MVNOs selling multi-network SIM-cards will publish their network list in which you can see which networks are available in which countries. Often, in small or exotic countries, fewer networks will be available. Make sure to check the networks and the networks and inquire about the available network technologies for each.
What are the benefits of Multi-Network SIM-cards?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Connectivity | Ability to switch between multiple networks for optimal signal and coverage. |
| Improved Reliability | Reduced downtime through network redundancy. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potential savings on roaming charges and better data plan options. |
| Scalability | Ease of adding or managing devices across various networks. |
Partnering with The IoT Guide
Curious to hear more about the possibilities of multi-network SIM-cards? Contact us for more information on the possibilities.

